Is wheel alignment the same as balancing?
Maintaining a vehicle involves numerous checks and services to ensure its optimal performance and longevity. Among these, wheel alignment and balancing are often misunderstood and conflated, despite serving different purposes. This essay aims to clarify the differences between wheel alignment and balancing, highlighting their unique functions, procedures, and benefits.
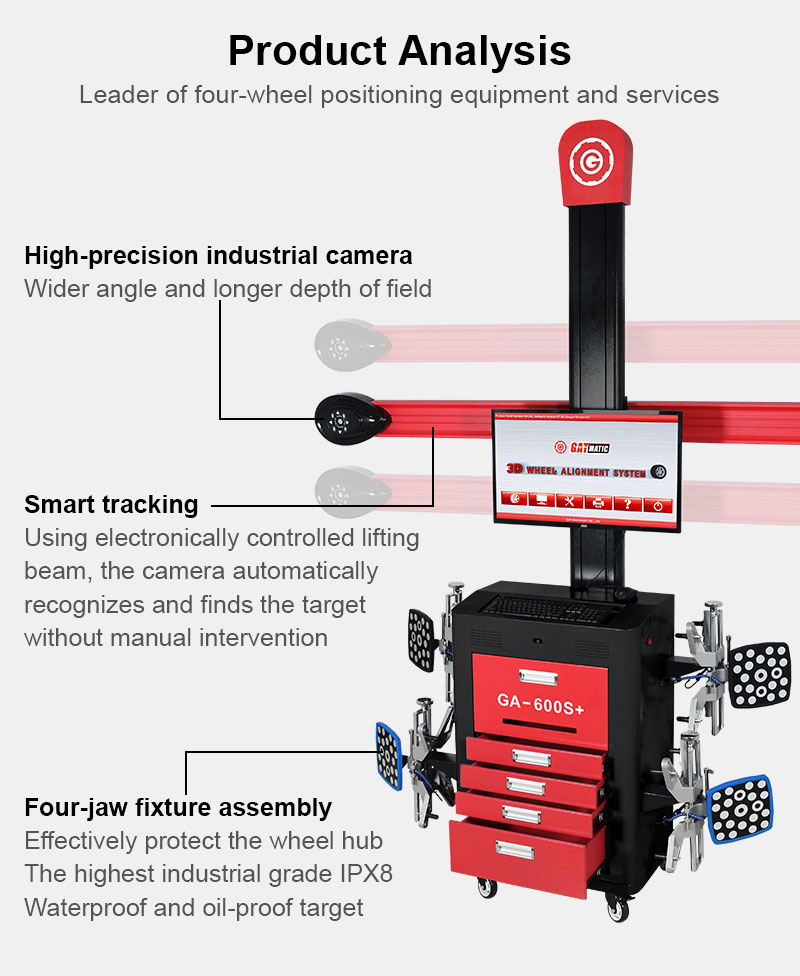
I. Definition and Purpose
Wheel alignment refers to the adjustment of the angles of the wheels to the car manufacturer’s specifications. The primary purpose of wheel alignment is to ensure that the vehicle drives straight, thereby reducing tire wear and improving overall handling and safety. Proper alignment involves precise adjustments to the car’s suspension system, affecting the angles at which the tires contact the road.
On the other hand, wheel balancing is the process of equalizing the weight distribution of the wheel and tire assembly. This procedure ensures that the wheels rotate smoothly without causing vibrations. Balancing is essential for a smooth ride and to prevent uneven tire wear, which can result from imbalances in the tire and wheel assembly.
II. Key Differences
The primary difference between wheel alignment and balancing lies in their functions. Alignment focuses on the direction and angles of the tires, ensuring they are set correctly relative to the vehicle’s frame. Misalignment can cause the vehicle to pull to one side, lead to uneven tire wear, and result in an off-center steering wheel. Conversely, balancing addresses the distribution of weight around the tire and wheel assembly. Imbalances can cause vibrations felt in the steering wheel, seat, or floorboard and lead to uneven tire wear.
The procedures for alignment and balancing are also distinct. Alignment involves adjusting the car’s suspension system, which is the system that connects a vehicle to its wheels. Mechanics use alignment machines to measure the wheel angles and make precise adjustments to bring them into the correct position. Balancing involves using a machine that spins the wheel and identifies any imbalances in weight. Mechanics then attach small weights to the rim to counterbalance any heavy spots, ensuring the wheel’s weight is evenly distributed.
III. Symptoms and Indicators
There are specific symptoms that indicate the need for alignment or balancing. If a vehicle is pulling to one side while driving, has uneven tire wear, or the steering wheel is off-center, it likely needs a wheel alignment. On the other hand, if the driver feels vibrations in the steering wheel, seat, or floorboard, especially at higher speeds, or notices uneven tire wear, the vehicle may need wheel balancing.
IV. When to Perform Each Service
Knowing when to perform these services is crucial for vehicle maintenance. Wheel alignment should generally be performed every 2-3 years or as specified by the manufacturer. Situations that necessitate alignment include hitting a curb or pothole or after performing suspension work. Regular checks are essential to maintain proper alignment and avoid excessive tire wear.
Wheel balancing is typically recommended every 6,000 to 8,000 miles or as specified by the manufacturer. It is especially necessary after replacing tires or when experiencing vibrations. Regular balancing ensures smooth operation and helps extend the life of the tires by preventing uneven wear.
V. Benefits of Proper Wheel Alignment and Balancing
The benefits of maintaining proper wheel alignment and balancing are numerous. Proper alignment enhances vehicle performance, increases tire lifespan, and improves fuel efficiency. It also ensures better handling and safety, reducing the risk of accidents caused by misaligned wheels. Similarly, balanced wheels provide a smoother ride, prevent vibrations, and contribute to even tire wear, further extending tire life and enhancing driving comfort.
Conclusion
In summary, while wheel alignment and balancing are often confused, they serve distinct and essential roles in vehicle maintenance. Alignment adjusts the angles of the wheels to ensure proper direction and handling, while balancing ensures the equal distribution of weight around the wheel and tire assembly. Both are crucial for maintaining vehicle performance, safety, and efficiency. Regular maintenance of wheel alignment and balancing not only enhances driving comfort but also prolongs the life of the tires and the vehicle itself. By understanding and addressing these different needs, drivers can ensure their vehicles remain in top condition.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between wheel alignment and balancing?
- A1: Wheel alignment adjusts the angles of the wheels to ensure they are perpendicular to the ground and parallel to each other, optimizing the vehicle’s handling and tire wear. Wheel balancing involves adding weights to the wheel to ensure the tire’s weight is evenly distributed around the axle, preventing vibrations and uneven tire wear.
Q2: How can I tell if my car needs a wheel alignment?
- A2: Signs that your car may need a wheel alignment include the vehicle pulling to one side, uneven or rapid tire wear, an off-center steering wheel when driving straight, and steering that feels loose or wandering.
Q3: What are the symptoms of unbalanced wheels?
- A3: Symptoms of unbalanced wheels include vibrations in the steering wheel, seat, or floorboard, especially at higher speeds, uneven tire wear, and increased noise while driving.
Q4: How often should I get a wheel alignment?
- A4: It is generally recommended to get a wheel alignment every 2-3 years or according to the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications. Additionally, an alignment should be performed after incidents like hitting a curb or pothole, or after suspension work.
Q5: How often should I have my wheels balanced?
- A5: Wheels should be balanced every 6,000 to 8,000 miles, or as specified by the vehicle manufacturer. It’s also advisable to balance the wheels when installing new tires or if you experience any of the symptoms of imbalance.
Q6: Can improper alignment affect my fuel efficiency?
- A6: Yes, improper alignment can cause increased rolling resistance, which forces the engine to work harder and use more fuel. Proper alignment helps in maintaining optimal fuel efficiency.
Describe Your Needs In Detail!
We will carefully evaluate your needs and give professional solutions.


